量子技術

- Photonics Equipment for Quantum Technologies
- Next-Day Availability
SPDC810N
Narrowband Correlated Photon-Pair Source
DNVB14
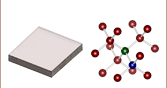
Single-Crystal Diamond with
Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers
SPDMA
Single Photon Detection Module with Adjustable Gain
VC2H2S
UHV Compatible Fiber Feedthrough for Ø2.75" CF Flange
FPQFA-5
Tunable Narrow Bandpass Fabry-Perot Filter

Please Wait
Thorlabs' Equipment for Quantum Technologies
Thorlabs provides an array of photonics equipment for quantum technologies and applications including:- Single Photon Sources, Detectors, and Counting Device
- Single-Crystal Diamonds with Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers
- Balanced Detectors with Excellent Common Mode Rejection
- Polaris® Mounts for High Precision and Long-Term Alignment Stability
- ORIC® Piezoelectric Intertia Drive Stages
- Optical Reference Cavities with Crystalline Mirrors
- Tunable, Narrow Bandpass Fabry-Perot Filters
- Turnkey, Ultra-Low-Noise Laser Systems
- High-Vacuum Compatible Viewports and Windows
- Ultra-High Vacuum Compatible Fiber Feedthroughs
- Sealed Vapor Reference Cells
- Educational and Concept Demonstration Kits for Quantum Mechanics
The technological world is currently in the middle of a quantum revolution. Rapid developments in the fields of quantum communication, computing, imaging, sensing, and simulation have leveraged counter-intuitive quantum mechanical concepts such as the uncertainty principle, superposition, and entanglement to realize new scientific discoveries and world-changing technologies. As advancements in quantum technology continue to be made, Thorlabs remains dedicated to providing the components necessary for photonics-based quantum applications. For any inquiries related to custom solutions, please contact Tech Support.
A selection of our products that are well-suited for quantum applications are shown in the table below; please click on the image for further details. See the Publications tab for a partial and growing list of articles which have utilized Thorlabs' products for research on quantum technologies and related applications.
Click to Enlarge
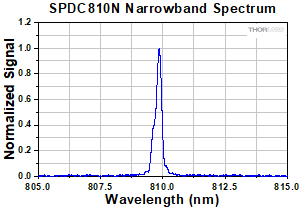
光源SPDC810Nからのシグナル光とアイドラ光のスペクトル。810 nmでオーバーラップしています。光子帯域幅(photon bandwidth)の半値全幅(FWHM)は<0.25 nm。
Click to Enlarge
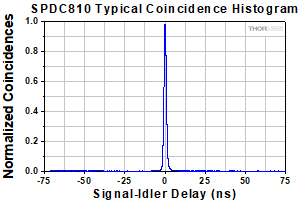
シグナル光子とアイドラ光子間の2次相関関数[g(2)(τ)]の測定結果 τ = 0におけるピークにより、光子対の生成が確認できます。データはどちらの光源でも有効です。
単一光子源
- 伝令付き単一光子源[gh(2)(τ = 0)< 0.1]
- 自発的パラメトリック下方変換(コリニア、タイプII)による光子対生成
- 光子帯域幅(Photon Bandwidth):<0.25 nm
- 光子対生成率:>450 kHz
- 405 nmの励起用レーザを内蔵
- 室温動作
相関光子対光源では、自発的パラメトリック下方変換(SPDC)技術を用いて、波長810 nm近傍の光子対を生成します。各光源には405 nmの励起(ポンプ)レーザが組込まれており、高い光子対生成率(Photon-Pair Generation Rate)が得られます。
狭帯域光源SPDC810Nでは、出力光の光子帯域幅(Photon Bandwidth)として0.25 nm、光子対生成率として100 kHz以上、伝令比率(Heralding Ratio)として高効率な0.30以上が得られます。これに対して光源SPDC810では、出力光の光子帯域幅は約10 nmと広いですが、光子対生成率として450 kHz以上、伝令比率として0.45とさらに高い値が得られます。
また、どちらの光源も伝令付き2次相関関数の遅延時間ゼロにおける値[g(2)(τ = 0)]として<0.1が得られるため、量子光学分野の用途に適した高輝度の伝令付き単一光子源として使用できます。
狭帯域光源SPDC810Nの非線形結晶の温度を調整して、出力される光子の波長を8 nm以上変化させることができます。これにより縮退についての調整が可能です。
| Item # | SPDC810N | SPDC810 |
|---|---|---|
| Photon Bandwidth | < 0.25 nm | ~10 nm |
| Max Pairs/Second | > 100 kHz | > 450 kHz |
| High-Efficiency Heralding Ratio (ηsi) | >0.30 | >0.45 |
| Wavelength Stability | ±0.1 nm | ±2.5 nm |
| Wavelength Tuning | > 8 nm | No |
| PC Control | Yes | Yes |
| On-Unit Front Panel Control | Yes | No |
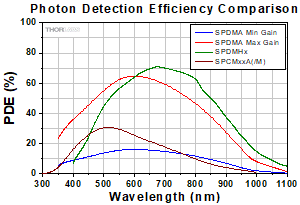
Click to Enlarge
モジュールSPDMAの利得を最大および最小にしたときのフォトン検出効率(PDE)と、モジュールSPDMHxおよびSPCMxxA(/M)のフォトン検出効率(PDE)の波長依存性を表示しています。動作波長範囲は、SPDMA:350 nm~1100 nm、SPDMHx:400 nm~1000 nm、SPCMxxA(/M):350 nm~900 nmです。
単一光子検出器(シングルフォトンディテクタ)
- 単一光子の検出用または計数用のモジュール
- 低いダークカウント
- 4種類の受光面サイズ:Ø20 µm、Ø50 µm、Ø100 µm、Ø500 µm
- アクティブクエンチング機能および温度安定化機能
当社では単一光子の検出用モジュールと計数用モジュールとして、フォトン検出効率(PDE)、ディテクタのサイズ、利得(固定/可変)、波長範囲などの異なる様々な製品をご用意しております。シングルフォトン検出モジュール(SPDMA)の波長域は350~1100 nmで、利得は連続的に調整できます。SMA端子からのTTL出力はオシロスコープや外部カウンタでモニタできます。一方、利得固定型のシングルフォトン検出モジュールSPDMHxの波長域は400~1000 nmですが、右のグラフに示すように近赤外域においてより高いフォトン検出効率(PDE)を有し、また最大ダークカウントレートも低くなっています。TTL出力パルスはLEMOコネクタからモニタできます。
シングルフォトンカウンターモジュールSPCMxxA/Mには31ビットのフォトンカウンタが内蔵されており、ディテクタの制御と出力読み取り用のソフトウェアパッケージが付属しています。波長範囲は350~900 nmです。

Click to Enlarge
SPCNTはシングルフォトン検出器SPDMAからのパルスのカウント数または周波数を表示します。
単一光子計数デバイス
- 組込みのディスプレイ画面またはPCで単一光子検出器からのカウント数をモニタ表示
- シングルフォトン検出器SPDMAおよびSPDMHxに対応
- ソフトウェアOptical Power Monitor を使用して測定値のモニタおよび測定結果の保存が可能
- モニタ出力は外部カウンタまたはオシロスコープに接続可能
- TRIG INコネクタへのTTL信号によるゲート機能
シングルフォトン計数デバイスSPCNTは、シングルフォトン検出器のSPDMAやSPDMHxシリーズ検出器と組み合わせることで、単一光子の検出から計数までの計測全体を行うことができるようになります。この計数用のデバイスは、接続された単一光子検出器からのパルス信号を受信し、結果を組込みのディスプレイ画面や解析用として接続されたPCのディスプレイ上に、カウント数または周波数として数値で表示します。
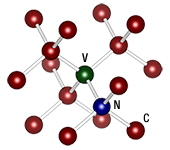
Click for Details
NV中心は、炭素格子における窒素とそれに隣接する空孔がペアになった欠陥です。
| Typical Quantum Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item # | DNVB1 | DNVB14 | ELSCxx |
| NV Center Density | 300 ppb | 4.5 ppm | < 0.03 ppb |
| Spin Coherence Time T2* a | 1 µs | 0.5 µs | - |
| Spin Coherence Time T2 b | 200 µs | 10 µs | - |
| Diamond Grade | Quantum | Quantum | Electronic |
窒素-空孔中心(NV中心)を有するダイヤモンド
- 化学気相成長法(CVD)により生成された単結晶ダイヤモンド
- 量子グレードまたは電子グレードのダイヤモンドをご用意
- NV中心の濃度は3種類ご用意
- DNVB1: 300 ppb
- DNVB14: 4.5 ppm
- ELSC20、ELSC40、ELSC45: < 0.03 ppb
こちらの単結晶ダイヤモンドは、Element Six社が特許を取得したプロセスによって製造し、量子研究の発展のために当社から提供されている製品です。磁場センシング、RF検出、ジャイロスコープ、メーザ、量子技術のデモンストレーション、量子計算、量子通信、および研究用途に適しています。量子グレードのダイヤモンドは、窒素-空孔中心(NV中心)の濃度300 ppbまたは4.5 ppmでご用意しております。欠陥中心をご自身で作成されたい場合は、NV濃度が0.03 ppb以下で、バックグラウンド不純物レベルが低い電子グレードのダイヤモンドもございます。これらのダイヤモンドは耐電離放射線性のデバイス製造などの用途にご使用いただけます。
差分ディテクタ
- ファイバ出射光または自由空間光の入力を選択可能
- ディテクタ:SiまたはInGaAs
- 最大帯域幅2.5 GHzまでのモデルをご用意
- 波長範囲:320 nm~1700 nm
- コモンモード除去比:> 35 dB(製品により異なります)
当社の差分フォトディテクタは、2つの光入力信号の差分をとることにより、コモンモード雑音を除去します。これにより、信号経路上の微弱な変化をノイズの中から取り出すことができます。各ディテクタにはよく整合された2つのSiまたはInGaAsの検出器と、超低ノイズのトランスインピーダンス増幅器が用いられています。ファイバ入力型の高速モニタ出力付き差分ディテクタには、FC/PCまたはFC/APCコネクタ用のアダプタが付いています。アダプタの取り外しが可能なタイプもあり、その場合は自由空間光の入力も可能です。また自由空間光用の差分ディテクタもご用意しており、その中には受光面の直径が5 mmの大きなディテクタもございます。
アバランシェフォトダイオードを使ったオートバランスディテクタは、低入力パワーの用途に適しています。このファイバ入力型ディテクタは1300 nmの波長に最適化されており、オートバランス検出モードでは、カットオフ周波数(調整可能)よりも低い周波数で変化する2つの光入力信号の光パワーの差を自動的に補償します。
| Polaris® Optic Mount Selection Guide | ||
|---|---|---|
| Optic Retention Method (Click Image to Enlarge) | Mount Type | Optic Sizes Available |
 Side Lock | Kinematic | Ø1/2", Ø19 mm, Ø25 mm, Ø1", Ø1.5", Ø50 mm, Ø2", Ø3" |
| Fixed | Ø1/2", Ø19 mm, Ø1", Ø2" | |
 SM Threaded | Kinematic | Ø1/2", Ø1", Ø2" |
 Low Distortion | Kinematic | Ø1/2", Ø19 mm, Ø25 mm, Ø1", Ø1.5", Ø50 mm, Ø2", Ø4", Ø6" |
| Fixed | Ø1/2", Ø1", or Ø2" | |
 Glue In | Kinematic | Ø1/2", Ø19 mm, Ø1" |
| Fixed | Ø1/2", Ø1", Ø2" | |
 Platform Mount | Kinematic | Platform Size: 1.80" x 1.80" (45.7 mm x 45.7 mm) |
Polaris®ミラーマウント
- ビームポインティングの長期安定性を目指した設計
- 温度によるヒステリシスの最小化
- クリーンルームおよび真空への対応
- 対応する光学素子のサイズ:Ø12.7 mm(Ø1/2インチ)~Ø152.4 mm(Ø6インチ)
- 4種類の光学素子保持方法と6種類のアジャスタをご用意
Polaris®シリーズは、アライメントの長期安定性を要求される量子実験用にお勧めの製品です。PolarisマウントはØ12.7 mm(Ø1/2インチ)~Ø152.4 mm(Ø6インチ)の大きさの光学素子に対応します。固定式とキネマティック式があり、また光学素子の保持方法も様々な方式からお選びいただけます。右のSelection Guideの表をご覧ください。さらに、全てのPolarisマウントと関連するアクセサリは、クリーンルームおよび真空に対応しています。
キネマティック式や固定式のPolarisマウントの中にはサイドホールドタイプの製品がありますが、その光学素子保持機構には2つのタイプがあります。1つはモノリシック構造のフレクシャーアームが付いた光学素子取付け穴を使うタイプで、これは特許取得済みの方式です。もう1つはフレクシャーバネと止めネジ(セットスクリュ)を組み合わせた方式です。これらの方式では光学歪みを最小限に抑えながら、高い保持力と優れたビームポインティングの安定性が得られます。マウント背面のアジャスタに水平方向からアクセスできないような限られたスペースに配置しなければならない場合には、上部調整機構(アジャスタ)付きのタイプをご利用いただけます。
SMネジ付きマウントの光学素子取付け穴にはSM05、SM1、またはSM2の内ネジが付いており、それらに対応する光学素子を取り付けることができます。
Polaris低歪みキネマティックミラーマウントには、キネマティック式と固定式のタイプがございます。これらは特許取得済みの3点接触プレートを採用しており、光学素子表面の歪みを低く抑えながら、ビームポインティングの安定性を長期的に保つことができます。光学素子と固定リングの間に挿入するインデックス付きウェーブワッシャにより、光学素子の曲げモーメントが除去され、また大きな温度変化があっても光学素子に加わる力が一定に保たれます。
接着タイプのミラーマウントにはキネマティック式と固定式光学接着剤を用いて光学素子を恒久的に固定する取付けセルがあるのが特徴です。この取付け方法では、従来の止めネジ(セットスクリュ)やフレクシャ機構による取り付け方に比べて光学表面の歪みが非常に小さくなります。
Polarisキネマティックプラットフォームマウントの取付け面は平坦で、オプトメカニクス部品取り付け用にM4タップ穴が9個、M4貫通穴が1個あります。その貫通穴と2個のタップ穴の両側にはアライメントピン用の穴が付いており、位置決めピンを使用して部品を精密に配置することができます。
| Accessories for Polaris Mounts |
|---|
| Ø1" Posts for Polaris Mirror Mounts |
| Polaris Clamping Arm |
| Polaris 45º Adapter |
アクティブなモニタとアライメントの長期安定性が求められる用途には、それに適したピエゾアジャスタ付きのキネマティックマウントがございます。ピエゾアクチュエータの駆動には、当社のベンチトップ型またはKinesis® K-Cube™のピエゾコントローラをお勧めいたします。
カスタム仕様のマウントをご要望の際には当社までお問い合わせください。
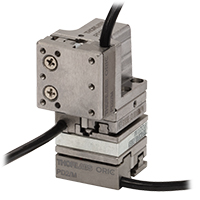
Click to Enlarge
Three PD2(/M) stages can be mounted in an XYZ configuration using the PD2T(/M) and PD2Z(/M) adapters.

Click to Enlarge
XY + rotation stage created by mounting a PDR1C(/M) rotation stage on a PD1D(/M) XY stage using a PD1Z(/M) right angle bracket.
ORIC® Piezoelectric Stages
- Compact Stainless Steel Stages with Piezo Inerta Drives
- Ideal for OEMs and Set-and-Hold Applications that Require Relative Positioning with High Resolution
- Translation Stages with:
- 5 mm Travel, Open- or Closed-Loop Linear Stages
- 20 mm Travel, Open- or Closed-Loop Linear Stages
- 50 mm Travel, Open-Loop Linear Stage
- Open- or Closed-Loop Rotation Stages
- Vacuum-Compatible Versions Suitable for Pressures Down to 10-6 Torr
Thorlabs' ORIC® piezoelectric inertia drive stages (U.S. Patent 11,606,045) provide fast and stable piezo-controlled motion with no backlash in compact stainless steel packages. The piezo inertia drive is self-locking when the stage is at rest and no power is supplied to the piezo, making these stages ideal for set-and-hold applications that require nanometer resolution and long-term alignment stability.
Linear translation stages are available with 5 mm travel, 20 mm travel, or 50 mm travel. These stages support open-loop positioning along a single axis, with the PD1D(/M) monolithic XY stage offering two-axis translation with ≤2 mrad orthogonality. The PDX2(/M) and PDX1(/M) incorporate optical encoders to provide 5 mm and 20 mm, respectively, of open- and closed-loop operation in single-axis packages. Right-angle brackets and the stackable design of the stages allow for the assembly of XY, XZ, and XYZ configurations.
Our piezo drive rotation stages offer continuous 360° rotation. The PDR1 series stages provide open-loop operation in standard and compact sizes, while the PDXR1(/M) includes an optical encoder which allows for open- and closed-loop operation. The rotation stages may be combined with ORIC 20 mm or 50 mm travel linear stages for XYΘ configurations.
We also offer vacuum-compatible versions of the 360° rotation stage and the 20 mm travel linear stage which can be used for pressures down to 10-6 Torr.
One of our piezo intertia controllers is required to operate these stages. Note that the piezo inertia drives cannot be driven using a standard piezo controller. Our K-Cube piezo controllers can be used to control either one (KIM001) or up to four (KIM101) piezo inertia drives in open-loop operation. The PDXC and PDXC2 piezo controllers support both open- and closed-loop operation. The PDXC controller provides three channels of control, while the PDXC2 controller provides a single channel of control in a compact design.
| ORIC® Piezo Inertia Stage Selection Guide | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Translation Stages | Rotation Stages | Vacuum-Compatible Stages | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 5 mm Translation Stage | 20 mm Translation Stages | 50 mm Translation Stage | Rotation Stages | Vacuum-Compatible Stages |
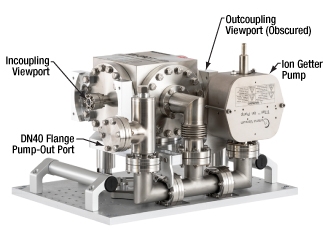
Click to Enlarge
XM-ORC Stainless Steel Vacuum Chamber and Ion Getter Pump

Click to Enlarge
Cylindrical Cavity with Optically-Contacted Crystalline-Coated Mirrors
Optical Reference Cavities
- High-Finesse Fabry-Perot Cavities for Active Frequency Stabilization
- Fused Silica, Crystalline-Coated Cavity Mirrors for Low Thermal Noise
- Includes an Ultra-Low Expansion (ULE®†) Cavity Spacer
- Available with 1064 nm, 1156 nm, 1397 nm, or 1550 nm Center Wavelength
- Integrated NTC and Peltier Elements for Active Temperature Control
- Includes Temperature Controller, Ion Getter Vacuum Pump, and Pump Controller
The XM-ORC Series of Optical Reference Cavities with Crystalline Mirrors are high-finesse Fabry-Perot cavities ideal for active frequency stabilization of a single mode CW laser. These optical cavities, designed together with Menlo Systems, integrate Thorlabs' high-performance supermirrors and are available with finesse values >200 000 at 1064 nm or >300 000 at 1156 nm, 1397 nm or 1550 nm. With a thermal noise Allan deviation (ADEV) limit as low as 1.6 x 10-16 and a low frequency drift of ~150 mHz/s, the XM-ORC reference cavities are ideal for applications that require cavity-stabilized lasers, such as high-resolution spectroscopy, quantum computing, and optical clocks. To inquire about custom reference cavities employing alternative geometries and operating at other center wavelengths, please see the full web presentation.
Optically Contacted Cavity
Each optical cavity includes a 12.1 cm cylindrical spacer made from ultra-low expansion (ULE) glass that is mounted horizontally on four support points within a sealed stainless steel vacuum housing. The incoupling and outcoupling cavity mirrors, which are concave and plano, respectively, are optically contacted and consist of Thorlabs' substrate-transferred crystalline coating (xtal stable™) on a fused silica substrate. ULE compensation rings are also included to ensure that room temperature operation will roughly correspond to the zero crossing of the thermal expansion coefficient for the assembled cavity.
†ULE is a registered trademark of Corning, Inc.
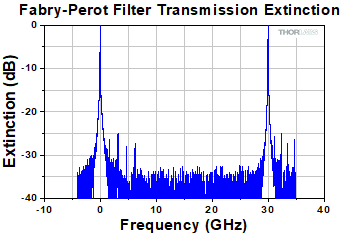
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Data
The Fabry-Perot filter transmits fundamental resonance modes at 30 GHz FSR and suppresses light off-resonance typically above -30 dB, not including higher order modes.

Click to Enlarge
The filters can be mounted in standard Ø1" kinematic mounts like the POLARIS-K1E shown here. A SM05-threaded mounted photodiode (Item # SM05PD2A) is attached to the filter's exit port for measurements up to 1100 nm (photodiode sold separately).
Tunable Narrow Bandpass Fabry-Perot Filters
- Operating Wavelength Range from 550 nm - 845 nm or 845 nm - 1300 nm
- Spectral Characterization of Quantum Emitters
- Free Spectral Range (FSR) of 30 GHz
- Transmission >80% for Low-Intensity Spectra Detection
- Finesse >300
- Resolution <100 MHz
- 5 mm Plano-Concave Cavity Mirror Separation
Thorlabs' FPQFA series Tunable Narrow Bandpass Fabry-Perot Filters are ideal for filtering low-light emission spectra over a narrow wavelength range of about 0.1 nm (for a 1 μm wavelength laser) or free spectral range (FSR) of 30 GHz. The Fabry-Perot filters are based on a non-confocal cavity composed of two high reflectivity mirrors, one planar and one spherical concave. The specific frequency transmitted by the cavity can be tuned by adjusting the length of the mirror separation using the built-in piezoelectric transducer. The filters have optical coatings for wavelength ranges from 550 - 845 nm (Item # FPQFA-5) and 845 nm - 1300 nm (Item # FPQFA-8), which are typical ranges for the photoluminescence spectra of Si1 and NV2 centers in diamond and InGaAs quantum dots3. The filter's >80% transmission, 30 GHz FSR, and <100 MHz resolution allow for the investigation of the spectral fine-structures of these low-light quantum emitters.
The filters can be used to select a part of the incoming light's spectrum, given by the Lorentzian-shaped transmittance characteristics, and use the spectrally filtered light down-stream in an optical system. Or the filters can be operated as scanning devices similar to the SA series FP interferometers, where the transmitted light is immediately measured using a photodiode, amplified by a transimpedance amplifier, and then displayed or recorded by an oscilloscope or data acquisition card. Several detector options are available from Thorlabs such as the SM05PD series mounted photodiodes, which can be attached to the filter's SM05-threaded exit port, or external detectors such as the DET series biased detectors, PDA series amplified detectors, or the APD series avalanche detectors.
References
- S. Lindner, A. Bommer, A. Muzha, A. Krueger, L. Gines, S. Mandal, O. Williams, E. Londero, A. Gali, and C. Becher "Strongly Inhomogeneous Distribution of Spectral Properties of Silicon-Vacancy Color Centers in Nanodiamonds", New J. Phys. 20, 115002 (2018)
- A. Savvin, A. Dormidonov, E. Smetanina, V. Mitrokhin, E. Lipatov, D. Genin, S. Potanin, A. Yelisseyev, and V. Vins, "NV– Diamond Laser", Nat Commun 12, 7118 (2021)
- A.B. Dey, M.K. Sanyal, I. Farrer, K. Permulal, D.A. Ritchie, Q. Li, J. Wu, and V. Dravid, "Correlating Photoluminescence and Structural Properties of Uncapped and GaAs-Capped Epitaxial InGaAs Quantum Dots", Sci Rep 8, 7514 (2018)

Click to Enlarge
レーザULN15TKは、4個のM6キャップスクリュを使用して光学テーブルに取り付け可能です。写真ではULN15TKの光出力部にPMファイバーパッチケーブルP3-1550PM-FC-5、アナログ変調ポートに3本のSMAケーブルCA2912がそれぞれ接続されています。
超低ノイズ単一周波数レーザーシステム、ベンチトップ型
- Cバンド用のターンキー式単一周波数レーザーシステム
- 中心波長:1550 nm ± 15 nm、ローレンツ線幅:100 Hz(典型値)
- 出力パワー(CW):120 mW(典型値)
- DC電流、AC電流、レーザ温度用のアナログ変調入力
- 電流変調帯域幅:20 MHz
- 長期安定性に優れた温度安定化筐体
- 内蔵のファイバーアイソレータ(アイソレーション:: 25 dB以上)が、後方反射光の影響を最小限に抑制
- USB 2.0を介したコマンドラインインターフェイスにより、リモート動作および設定値の調整が可能
当社のターンキー式超低ノイズ(ULN)レーザーシステムULN15TKにはレーザULN15PCが内蔵されており、すぐにお使いいただけます。特許取得済みのファイバーブラッググレーティング(FBG)をベースに設計されており、ベンチトップ型の筐体内には低ノイズドライバと温度安定化装置があります。こちらのターンキー式レーザーシステムは、-160 dBc/Hz以下の相対強度ノイズと、100 Hz以下の典型的な(ローレンツ型)線幅を有する単一周波数の光を出力します。レーザは出荷時に性能が最適化されており、120 mWの光出力と70 dBサイドモード抑圧比(SMSR)を有します(どちらも典型値)。このような狭線幅のレーザ光が、特に外部光共振器に結合されて使用されると、光時計の開発や中性原子量子計算での使用に適します。
このレーザは、FC/APCバルクヘッド(2.0 mmナローキー)出力コネクタネクタ付きのファイバ出力型です。最良の性能を得るために、PM1550-XPファイバを内蔵したP3-1550PM-FC-1のような偏波保持FC/APCファイバーパッチケーブルのご使用をお勧めいたします。
レーザULN15PCの侠線幅を達成するために、ターンキー式ULNレーザには電流ノイズを最小限に抑えるように設計された駆動電子回路が付属します。また、この駆動電子回路にはレーザ内部の温度設定を制御する熱安定化システムも付属しており、システムを標準的な実験室の環境での使用にあたり、出力と波長の長期安定性を発揮します。レーザの出力部には、レーザの後方反射の影響を最小化するためのファイバーアイソレータも内蔵されています。
真空用コンポーネント
- 高真空用Ø2.75インチCFフランジビューポートおよびウィンドウ
- 超高真空用Ø2.75インチCFフランジファイバーフィードスルー
- Ø25.4 mm(Ø1インチ)のフラットウィンドウ、Ø38.1 mm(Ø1.5インチ)のフラットまたはウェッジ付きウィンドウから選択可能
- 当社のオプトメカニクス部品に対応
当社では高真空対応のCF(コンフラット)ビューポート、フランジ、それらに関連する部品やハードウェアのラインナップを拡大しています。高真空(HV)システムは10-8 Torrまでの真空を保持できます。当社のØ2.75インチの高真空用CFビューポートは、金属とガラス間をシールするのにバイトンOリングを使用しており、その最高ベーキング温度は150 °C、最大加熱速度は20 °C/minです。Ø25.4 mm(Ø1インチ)ウィンドウ用のビューポートは、標準品として3種類の素材(サファイア(200 nm~4.5 μm)、CaF2 (180 nm~8.0 μm)、UVFS (185 nm~2.1 μm)からお選びいただけます。いずれもコーティングはされていません。付属のウィンドウは、当社の厚さ4.9~5.15 mmのØ25.4 mm(Ø1インチ)フラットウィンドウと交換することも可能です。Ø38.1 mm(Ø1.5インチ)のフラットウィンドウまたはØ38.1 mm(Ø1.5インチ)のウェッジ付きウィンドウのビューポートもございます。これらのビューポートとしてはUVFSウィンドウ付きの製品をご用意しておりますが、コーティング無しのタイプ、または4種類の標準的な低損失広帯域反射防止コーティングの中の1種類を両面に施したタイプからお選びいただけます。
当社のオプトメカニクスに対応するØ2.75インチの高真空用CFビューポートもございます。4つの#4-40取付け穴を用いて30 mmケージシステムを取り付けることができ、またSM内ネジを用いてレンズチューブシステムを取付けることもできます。また、 Ø25.4 mm(Ø1インチ)ウィンドウ用ビューポートには#2-56取付け穴が4つあり、これらを用いてFiberPortコリメータを直接ビューポートに取り付けることができます。
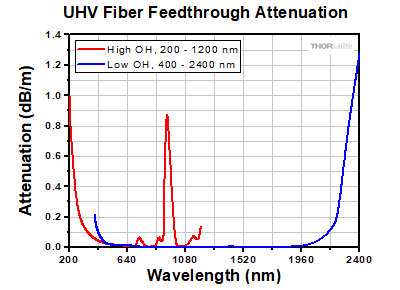
Click to Enlarge
Click for Data
超高真空用CFフランジのフィードスルーに使用されているファイバの損失特性データ(計算値)
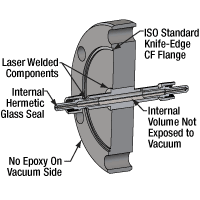
Click to Enlarge
超高真空用ファイバーフィードスルーCFフランジの断面図
当社ではØ2.75インチファイバーフィードスルーCFフランジもご提供しており、 これを用いると10-10 Torrまでの超高真空(UHV)システム内の光学系との光結合が可能になります。フィードスルーにはハーメチックシールされたステップインデックスマルチモードファイバがステンレススチール製シェル内に組み込まれています。挿入損失は≤2.3 dBと小さく、最大入射光パワーは1 W、最高ベーキング温度は250 °Cです。フィードスルーとして、コア径はØ100 μm、Ø200 μm、Ø400 μm、Ø600 μm、波長範囲は高OHの200~1200 nm用と低OHの400~2400 nm用のファイバをご用意しています。ファイバーフィードスルーの両端にはオス型SMA905コネクタが付いています。ファイバーパッチケーブルを接続するために、アダプタをご使用いただくことができます。 フィードスルーの真空側では、真空対応のパッチケーブルを接続するために真空対応SMA-SMAアダプタADASMAVをご使用いただけます。
Ø2.75インチCFフランジ用の銅製ガスケットや取付け用部品セットもご用意しています。

Click to Enlarge
The GC19100-I quartz vapor reference cell contains iodine (I) vapor and has wedged UVFS windows to eliminate etalon effects.

Click to Enlarge
The GC25075-RB vapor reference cell contains rubidium (Rb) and is fabricated from borosilicate glass, a rugged material known to resist chipping and cracking.
Vapor Reference Cells
- Sealed Glass Cells with Vapors of Specific Elements
- Borosilicate Glass Reference Cells
- Cesium (Cs)
- Potassium (K)
- Sodium (Na)
- Rubidium (Rb)
- Quartz Glass Reference Cells
- Cesium (Cs)
- Iodine (I)
- Rubidium (Rb)
- Enhanced Rubidium 87 (87Rb)
Thorlabs offers sealed glass reference cells that contain vapors of specific atomic elements or molecular compounds, each of which has a well-defined absorption spectrum. These cells may be used for the stabilization of laser frequencies, in quantum memory systems, and in magnetometry. They also have spectroscopic applications such as tunable diode laser calibration, the calibration of wavelength meters, and as elements in magneto-optical traps for atomic cooling. Both borosilicate and quartz reference cells are available with a range of standard fill materials. All of the cells that we offer are baked and evacuated to
10-8 Torr in order to remove contaminants prior to filling. Additionally, each cell is helium leak checked to ensure the longevity of the vapor cell. Custom reference cells can be manufactured upon request.
Our borosilicate glass reference cells are available from stock with cesium (Cs), potassium (K), sodium (Na), or rubidium (Rb) vapor. These cells are tested to ensure that the transmission through the cell exceeds 84% for light in the 350 nm to 2.2 μm range. The cells are 71.8 mm (2.83") long and have an outer diameter of 25.4 mm (1.00") with a >20.0 mm (>0.79") clear aperture.
Quartz reference cells are available from stock with cesium (Cs), iodine (I), rubidium (Rb), or enhanced rubidium 87 (87Rb) vapor. These cells feature UV fused silica windows for superior transmission in the UV spectral range. The windows, which are angled to compensate for beam offset, are designed with a 2 degree wedge so as to eliminate etalon effects. The outer diameter of the cells is 19.0 mm (0.75"). Cesium, rubidium and enhanced rubidium cells have a length of 75.0 mm (2.95"), while the iodine reference cell has a length of 100.0 mm (3.94").
教育用キット
- 教育、実習、授業用
- 基本的な量子光学現象の観察
- エンタングル(量子もつれ)した光子対の生成とその量子力学特性を調べるための、自由空間光学系による実践的なセットアップ
- 相補性、経路情報、重ね合わせといった量子力学の原理についての古典論的疑似実験
- 量子暗号の基本原理についての古典論的疑似実験
- 必要なハードウェアに加えて詳細なマニュアルと教材が含まれたキット
- 組み立て・使用方法が簡単
教育用実験キットシリーズは、多くの古典的な実験のほか、新しい研究分野や量子技術からテーマを取り上げ、物理学、光学、フォトニクスなどの学習や研究を促進することを目的としています。いずれの教育用キットにも必要なコンポーネントが含まれており、また詳しいセットアップの手順だけでなく教育内容も盛り込まれたマニュアルが付属しています。これらのキットの価格は含まれるコンポーネントの合計金額で設定されており、付属の教材は無料でご提供しています。 製品購入前あるいは購入後にかかわらず、技術的サポートが必要な場合は当社までご相談ください。
量子光学用教育キット
当社の量子光学用教育キットは、光の量子的特性を直に探求できるように設計されており、開放的でアクセスしやすいシステムになっています。光子対を生成するためのtype-I BBO結晶から最先端のシングルフォトンディテクタに至るまで、すべてに自由空間光学素子を採用することで、測定が行われる位置とタイミングを明確にすることができます。このキットでは、単一光子の干渉実験や単一光子による量子消しゴム(Quantum Eraser)実験など、いくつかの実験を行うことができます。単一光子が放出される円錐形の方向を模擬する可視(VIS)レーザを用いて、アライメント方法を順を追って説明することで、実験のセットアップ時間を短縮することができます。このキットの特に重要な目的の一つは、何が非古典的な光源の構成要素になっているかを学習することです。キットEDU-QOP1/Mは光学テーブルまたはブレッドボード上に取付ける必要がありますが、それらはこのキットには含まれておりませんのでご注意ください。製品に適したブレッドボードをお持ちでない場合には、光学ブレッドボードB60120AXにダンピング脚AV5/Mを取付けてご使用いただくことをお勧めします。
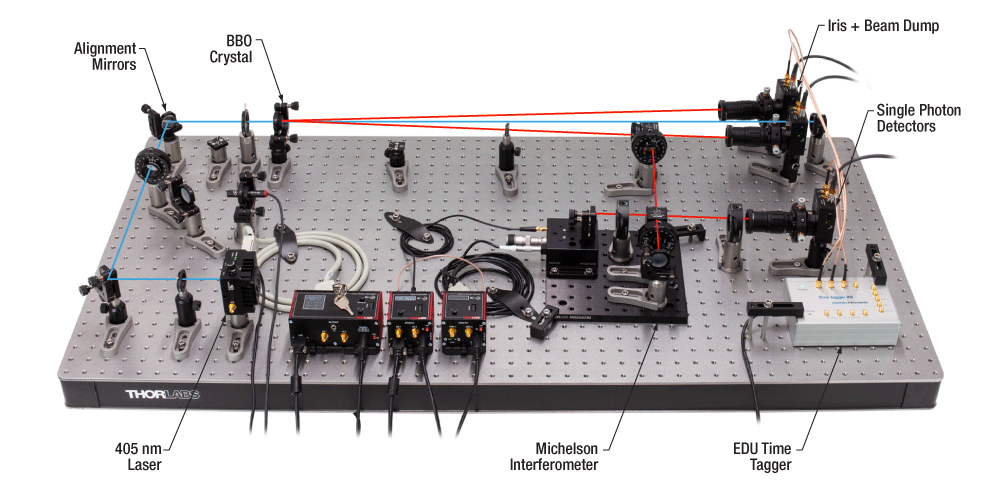
量子光学用教育キットを使用した、単一光子による量子消しゴム(Quantum Eraser)実験のセットアップ(ブレッドボードはキットには含まれません)
量子消しゴム(Quantum Eraser)実習キット
量子消しゴム実習キットでは、相補性、経路情報、重ね合わせといった量子力学の原理を例証することができます。この量子力学実験では、まず単一光子をマッハツェンダ干渉計に入射します。次に直線偏光子を用いて光子が水平・垂直のどちらの偏光状態にあるかを「マーキング」しますが、これは光子が干渉計のどちら側を通ったかを示すことになります。干渉パターン(波動性)と経路情報(粒子性)は同時に観測できないため、このように経路情報を観測すると干渉パターンは消失します。3つ目の直線偏光子を2つのビームを重ねた後に置くと、経路情報が「消去」されるため干渉パターンが復活します。本来の量子消しゴム実験では単一光子が使われますが、キットEDU-QE1/Mでは緑色の連続発振(CW)レーザ光源を使用しているためビーム経路が裸眼で見えます。従って、この実験結果は光の偏光という古典的性質で説明できますが、上記の量子力学的説明は単一光子実験のアナロジーになっています。
量子暗号疑似実習用キット
当社の量子暗号疑似実習用キットでは、様々な実験を通して量子暗号および暗号化プロトコルBB84の基本事項を実習することを目指しています。これらの実験により、光の偏光状態を利用してメッセージをバイナリにエンコードし、BB84プロトコルで暗号化する方法を学ぶことができます。なお、量子暗号疑似実習用キットEDU-QCRY1/Mでは、パルスレーザ光、つまり古典的な光を使用しています。プロトコルのシーケンスは真の量子暗号化システムと全く同じですが、完全な暗号システムとしてご使用いただけるわけではありません。
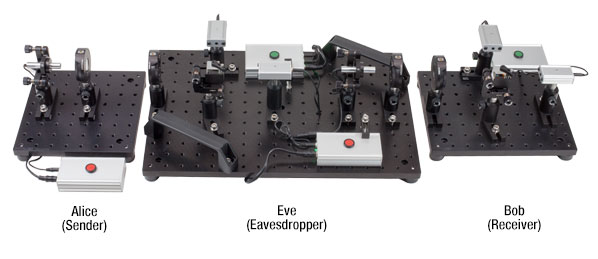
Click to Enlarge
当社の量子暗号疑似実習用キットでは、量子暗号および暗号化プロトコルBB84の基本事項を学習することができます。
Select Publications
2023
A. Al-Juboori, H.Z.J. Zeng, M.A.P. Nguyen, X. Ai, A. Laucht, A. Solntsev, M. Toth, R. Malaney, and I. Aharonovich, "Quantum Key Distribution Using a Quantum Emitter in Hexagonal Boron Nitride," Adv. Quantum Technol. 6, 9 (2023)
» Products Cited: FBR-AH1, FBRP, EO-AM-NR-C1, HVA200, PBS052
C. Li, J. Jang, T. Badloe, T. Yang, J. Kim, J. Kim, M. Nguyen, S.A. Maier, J. Rho, H. Ren, and I. Aharonovich, "Arbitrarily structured quantum emission with a multifunctional metalens," eLight 3, 19 (2023)
» Products Cited: CPS635, LPVISE100-A, AHWP10M-600, TTL180-A
2022
Y. Bloom, I. Fields, A. Maslennikov, and G.G. Rozenman, "Quantum Cryptography—A Simplified Undergraduate Experiment and Simulation," Physics 4, 104-123 (2022)
» Products Cited: EDU-QCRY1(/M)
2021
D. Lowndes, S. Frick, A. Hart, and J. Rarity, "A low cost, short range quantum key distribution system," EPJ Quantum Technol., 8 15 (2021)
» Products Cited: WPQ05M-633, WPH05M-633, DDR25, FBH650-10
P. Bevington, R. Gartman, and W. Chalupczak , "Object detection with an alkali-metal spin maser," J. Appl. Phys. 130, 214501 (2021)
» Products Cited: PDB150A
S. Lee, S.-B. Lee, S.E. Park, H.-G. Hong, M.-S. Heo, S. Seo, J. Jeong, T.Y. Kwon, and G. Moon, "Compact modulation transfer spectroscopy module for highly stable laser frequency," Opt. Lasers Eng. 146, 106698 (2021)
» Products Cited: PDA10A2, POLARIS-K05S1, POLARIS-K1-2AH
J.S. Stuart, M. Hedges, R. Ahlefeldt, and M. Sellars, "Initialization protocol for efficient quantum memories using resolved hyperfine structure," Phys. Rev. Res. 3, L032054 (2021)
» Products Cited: FPL1009S
D. Main, T.M. Hird, S. Gao, E. Oguz, D.J. Saunders, I.A. Walmsley, and P.M. Ledingham, "Preparing narrow velocity distributions for quantum memories in room-temperature alkali-metal vapors," Phys. Rev. A 103, 043105 (2021)
» Products Cited: APD120
P.C. Fariña, B. Merkel, N.H. Valencia, P. Yu, A. Ulanowski, and A. Reiserer, "Coherent Control in the Ground and Optically Excited States of an Ensemble of Erbium Dopants," Phys. Rev. Appl. 15, 064028 (2021)
» Products Cited: PDB570C, GRIN2915, SMPF0215
J. Shi, W. Sun, H. Utzat, A. Farahvash, F.Y. Gao, Z. Zhang, U. Barotov, A.P. Willard, K.A. Nelson, and M.G. Bawendi, "All-optical fluorescence blinking control in quantum dots with ultrafast mid-infrared pulses," Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1355-1361 (2021)
» Products Cited: WP25H-K
F.M. Stürner, A. Brennis, T. Buck, J. Kassel, R. Rölver, T. Fuchs, A. Savitsky, D. Suter, J. Grimmel, S. Hengesbach, M. Förtsch, K. Nakamura, H. Sumiya, S. Onoda, J. Isoya, and F. Jelezko, "Integrated and Portable Magnetometer Based on Nitrogen-Vacancy Ensembles in Diamond," Adv. Quantum Technol. 4, 2000111 (2021)
» Products Cited: PM-S405-XP
S. Kanthak, M. Gebbe, M. Gersemann, S. Abend, E.M. Rasel, M. Krutzik, "Time-domain optics for atomic quantum matter," New J. Phys. 23, 093002 (2021)
» Products Cited: IO-5-1064-VHP, TC25FC-1064
2020
V.K. Sewani, H.H. Vallabhapurapu, Y. Yang, H.R. Firgau, C. Adambukulam, B.C. Johnson, J.J. Pla, and A. Laucht, "Coherent control of NV-centers in diamond in a quantum teaching lab," Am. J. Phys. 88, 1156–1169 (2020)
» Products Cited: LP520-SF15, DET025AFC(/M), MBT616D(/M), DMLP550, C280TMD-A
R.L. Patel, L.Q. Zhou, A.C. Frangeskou, G.A. Stimpson, B.G. Breeze, A. Nikitin, M.W. Dale, E.C. Nichols, W. Thornley, B.L. Green, M.E. Newton, A.M. Edmonds, M.L. Markham, D.J. Twitchen, and G.W. Morley, "Subnanotesla Magnetometry with a Fiber-Coupled Diamond Sensor", Phys. Rev. Applied 14, 044058 (2020)
» Products Cited: PDB450A, BSF10-A, FG400AEA, SM1NR05, C171TMD-B, C330TMD-B
H. Zheng, Z. Sun, G. Chatzidrosos, C. Zhang, K. Nakamura, H. Sumiya, T. Ohshima, J. Isoya, J. Wrachtrup, A. Wickenbrock, and D. Budker, "Microwave-Free Vector Magnetometry with Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers along a Single Axis in Diamond," Phys. Rev. Applied 13, 044023 (2020)
» Products Cited: PDA36A, PT3-Z8 (PT3/M-Z8), NR360S
S. Kulkarni, A. Uminska, J. Gleason, S. Barke, R. Ferguson, J. Sanjuán, P. Fulda, and G. Mueller, "Ultrastable optical components using adjustable commercial mirror mounts anchored in a ULE spacer," Appl. Opt. 59, 6999-7003 (2020)
» Products Cited: POLARIS-K1T1
S. Prabhakar, T. Shields, A.C. Dada, M. Ebrahim, G.G. Taylor, D. Morozov, K. Erotokritou, S. Miki, M. Yabuno, H. Terai, C. Gawith, M. Kues, L. Caspani, R.H. Hadfield, and M. Clerici, "Two-photon quantum interference and entanglement at 2.1 µm," Sci. Adv. 6, eaay5195 (2020)
» Products Cited: PDA10DT(-EC)
M. Kutas, B. Haase, P. Bickert, F. Riexinger, D. Molter, and G. von Freymann, "Terahertz quantum sensing," Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz8065 (2020)
» Products Cited: CS2100M-USB
2019
S. Ecker, F. Bouchard, L. Bulla, F. Brandt, O. Kohout, F. Steinlechner, R. Fickler, M. Malik, Y. Guryanova, R. Ursin, and M. Huber, "Overcoming Noise in Entanglement Distribution," Phys. Rev. X 9, 041042 (2019)
» Products Cited: DET10A(/M)
2018
J.A. Zielinska and M.W. Mitchell, "Atom-resonant squeezed light from a tunable monolithic ppRKTP parametric amplifier," Opt. Lett. 43, 643-646 (2018)
» Products Cited: PDB450A
S. Wei, D. Wang, J. Lin, and X. Yuan., "Demonstration of orbital angular momentum channel healing using a Fabry-Pérot cavity," Opto-Electron. Adv. 1, 180006 (2018)
» Products Cited: SA200-5B, SA201(-EC), MDT694B
P.-J. Tsai and Y.-C. Chen, "Ultrabright, narrow-band photon-pair source for atomic quantum memories," Quantum Sci. Technol. 3, 034005 (2018)
» Products Cited: SA200-8B, PDA100A(-EC)
S. Tamura, K. Ikeda, K. Okamura, K. Yoshii, F.-L. Hong, T. Horikiri, and H. Kosaka, "Two-step frequency conversion for connecting distant quantum memories by transmission through an optical fiber," Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57, 062801 (2018)
» Products Cited: HL63142DG
P. Vernaz-Gris, K. Huang, M. Cao, A.S. Sheremet, and J. Laurat, "Highly-efficient quantum memory for polarization qubits in a spatially-multiplexed cold atomic ensemble," Nat. Commun. 9, 363 (2018)
» Products Cited: BD40
A. Dréau, A. Tchebotareva, A. El Mahdaoui, C. Bonato, and R. Hanson, "Quantum Frequency Conversion of Single Photons from a Nitrogen-Vacancy Center in Diamond to Telecommunication Wavelengths," Phys. Rev. Appl. 9, 064031 (2018)
» Products Cited: S122C
2017
B. Docters, J. Wrachtrup, and I. Gerhardt, "Two Step Excitation in Hot Atomic Sodium Vapor," Sci. Rep. 7, 11760 (2017)
» Products Cited: C220TME-A, PM200, S130C, PDA36A(-EC)
K.I. Gerasimov, M.M. Minnegaliev, S.A. Moissev, R.V. Urmancheev, T. Chanelière, and A. Louchet-Chauvet, "Quantum memory in an orthogonal geometry of silenced echo retrieval," Opt. Spectrosc. 123, 211-216 (2017)
» Products Cited: DET100A(/M), APD102A(/M)
2016
A. Kinos, Q. Li, L. Rippe, and S. Kröll, "Development and characterization of high suppression and high étendue narrowband spectral filters," Appl. Opt. 55, 10442-10448 (2016)
» Products Cited: PDB150A
S.L. Portalupi, M. Widmann, C. Nawrath, M. Jetter, P. Michler, J. Wrachtup, and I. Gerhardt, "Simultaneous Faraday filtering of the Mollow triplet sidebands with the Cs-D1 clock transition," Nat. Commun. 7, 13632 (2016)
» Products Cited: GT10-B
R.A. Jensen, I.-C. Huang, O. Chen, J.T. Choy, T.S. Bischof, M. Loncar, and M.G. Bawendi, "Optical Trapping and Two-Photon Excitation of Colloidal Quantum Dots Using Bowtie Apertures," ACS Photonics 3 (3), 423-427, (2016)
» Products Cited: MAX301(/M), DET50B(/M)
B. Sotillo, V. Bharadwaj, J.P. Hadden, M. Sakakura, A. Chiappini, T.T. Fernandez, S. Longhi, O. Jedrkiewicz, Y. Shimotsuma, L. Criante, R. Osellame, G. Galzerano, M. Ferrari, K. Miura, R. Ramponi, P.E. Barclay, and S.M. Eaton, "Diamond photonics platform enabled by femtosecond laser writing," Sci. Rep. 6, 35566 (2016)
» Products Cited: MBT401D(/M), S1FC808, TLS001-635
A. Sipahigil, R.E. Evans, D.D. Sukachev, M.J. Burek, J. Borregaard, M.K. Bhaskar, C.T. Nguyen, J.L. Pacheco, H.A. Atikian, C. Meuwly, R.M. Camacho, F. Jelezko, E. Bielejec, H. Park, M. Loncar, and M.D. Lukin, "An integrated diamond nanophotonics platform for quantum-optical networks," Science 354, 847-850 (2016)
» Products Cited: PDA100A(-EC), LCC3112H/M, LP705-SF15, GVS012(/M)
2014
I.I. Vlasov, A.A. Shiryaev, T. Rendler, S. Steinert, S.-Y. Lee, D. Antonov, M. Vörös, F. Jelezko, A.V. Fisenko, L.F. Semjonova, J. Biskupek, U. Kaiser, O.I. Lebedev, I. Sildos, P.R. Hemmer, V.I. Konov, A. Gali, and J. Wrachtrup, "Molecular-sized fluorescent nanodiamonds," Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 54-58 (2014)
» Products Cited: HL6548FG, HL6738MG
2013
M. Sabooni, S. Tornibue Kometa, A. Thuresson, S. Kröll, and L. Rippe, "Cavity-enhanced storage—preparing for high-efficiency quantum memories," New J. Phys. 15, 035025 (2013)
» Products Cited: PDB150A
2012
K.F. Reim, J. Nunn, X.-M. Jin, P.S. Michelberger, T.F.M. Champion, D.G. England, K.C. Lee, W.S. Kolthammer, N.K. Langford, and I.A. Walmsley, "Multipulse Addressing of a Raman Quantum Memory: Configurable Beam Splitting and Efficient Readout," Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 263602 (2012)
» Products Cited: APD210
2009
A. Walther, A. Amari, S. Kröll, and A. Kalachev, "Experimental superradiance and slow-light effects for quantum memories," Phys. Rev. A 80, 012317 (2009)
» Products Cited: PDB150A
| Posted Comments: | |
| No Comments Posted |
 Products Home
Products Home